Description
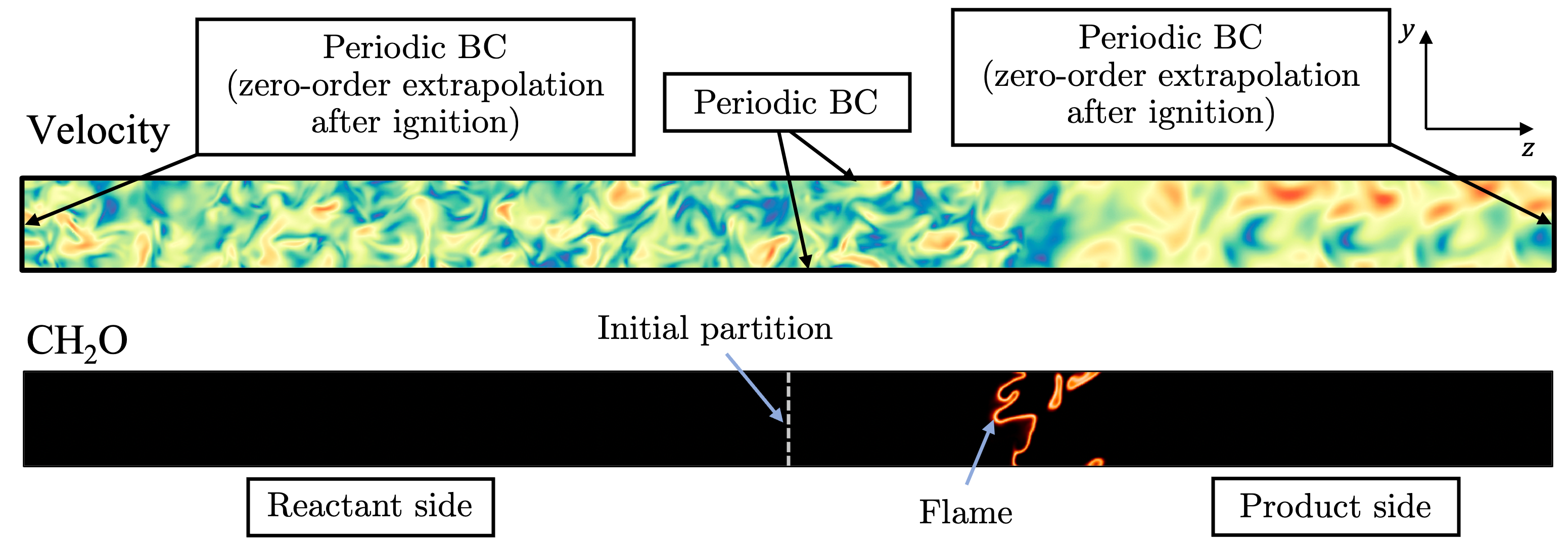
TThe DNS study involves a statistically steady, isotropic, and homogeneous turbulent flow in an unconfined space. The flame is initialized by a planar surface separating half of the domain containing methane/air mixture at 700 K and 3.04 × 107 erg cm−3 pressure, and another half with hot products, and is immersed in a high-intensity turbulent flow field with Kolmogorov type spectrum. The idea is to investigate the process of flame interaction with steady homogeneous isotropic turbulence. However, the flow needs to be constantly stirred at the largest scale to ensure a steady energy cascade to smaller scales so that the turbulence-flame interaction at the quasi-steady state can be studied. A spectral turbulence- driving method is used in the study, the details of which are available in Poludnenko and Oran. This driving method produces statistically steady forced-HIT flows with arbitrarily complex energy spectra. In particular, it is possible to achieve Kolmogorov type turbulence with inertial range of energy cascade extending up to energy injection scale. The other advantage of this method is that it does not introduce any artificial large-scale anisotropy, compression, or rarefaction. Prior to ignition, all domain boundaries are periodic. At ignition, boundary conditions along the left and right z-boundaries (as shown in Figure 9) are switched to zero-order extrapolation to prevent any non-physical pressure build-up in the domain and the formation of artificial large-scale rarefaction waves at the boundaries.
The computational domain aspect ratio is 1 × 1 × 16, with a grid size of 257 × 257 × 4097, including 16 grid points per unit laminar flame thermal thickness. The cell size is 2.62 × 10−4 cm. The turbulent velocity at energy injection scale (L = 0.067 cm) length scale is 213.92 cms−1 with turbulent root-mean-squared (RMS) velocity of 245.83 cms−1, resulting in an eddy turnover time of 3.14×10−4 s. The same velocity quantities corresponding to the integral length scale (l = 0.0196 cm) are 141.93 cms−1 and 132.2 cms−1. The ignition delay time of the mixture is three times the eddy turn-over time, and the total simulation runtime is 16 times the eddy turn-over time. The Damköhler and Karlovitz numbers are 0.66 and 9.97, respectively.
The DNS calculation is performed using the code Athena-RFX, which implements higher-order fully conservative Godunov-type methods for integration of fluid equations. The numerics in this work are third-order accurate in space and second-order accurate in time. More details are available in the original paper. The foundational fuel chemistry model (FFCM-1) with 22 species and 107 reactions is used as the chemical mechanism.
Quick Info
- Kaggle Link
- Contributors: Alexei Y. Poludnenko
- Nx = 257, Ny = 257, Nz = 4097, Nɸ = 6 + 21
- Size = 30 GB
- DOI
- .bib
- info.json